GPT-5 has just arrived, and it’s making waves as one of the most impressive AI models for coding and software development to date. With an extended context window, enhanced reasoning, and coding capabilities, this model promises to revolutionize how developers build, test, and deploy applications. In this article, I’m going to take you through an extensive hands-on journey with GPT-5, exploring its ability to handle complex coding tasks, automated testing, multimodal inputs, API testing, and even UI design—all while maintaining a sharp focus on precision and usability.
From debugging a challenging web application to generating sophisticated automated tests and creating a stunning landing page, this exploration will showcase GPT-5’s strengths, limitations, and potential impact on the future of automated software testing. So buckle up as we dive deep into the world of GPT-5 and its game-changing capabilities.
Table of Contents
- GPT-5’s Impressive Benchmark Performance and Pricing
- Putting GPT-5 to the Test: Debugging a Complex Web Application
- Automated UI Testing with Playwright: Successes and Struggles
- Multimodal Testing: Generating Tests from Images
- Automated API Testing from Postman Collections
- Designing a Beautiful Landing Page with Automated Tests
- Final Thoughts on GPT-5’s Capabilities and Future Potential
- Frequently Asked Questions about GPT-5
GPT-5’s Impressive Benchmark Performance and Pricing
Before diving into practical demonstrations, it’s essential to understand the foundation of GPT-5’s capabilities. According to recent benchmarks and livestreams, GPT-5 offers a massive 400,000 token context window and an output window of 128,000 tokens. This means it can handle and remember far more information during a single interaction than previous models, making it ideal for complex coding and multi-step tasks.
In terms of pricing, GPT-5 comes in at a competitive rate, with input tokens priced at $1.25 per thousand and output tokens at $10 per thousand. This pricing structure makes it accessible for extended use without the prohibitive costs associated with some other pro licenses, which can reach $200 monthly.
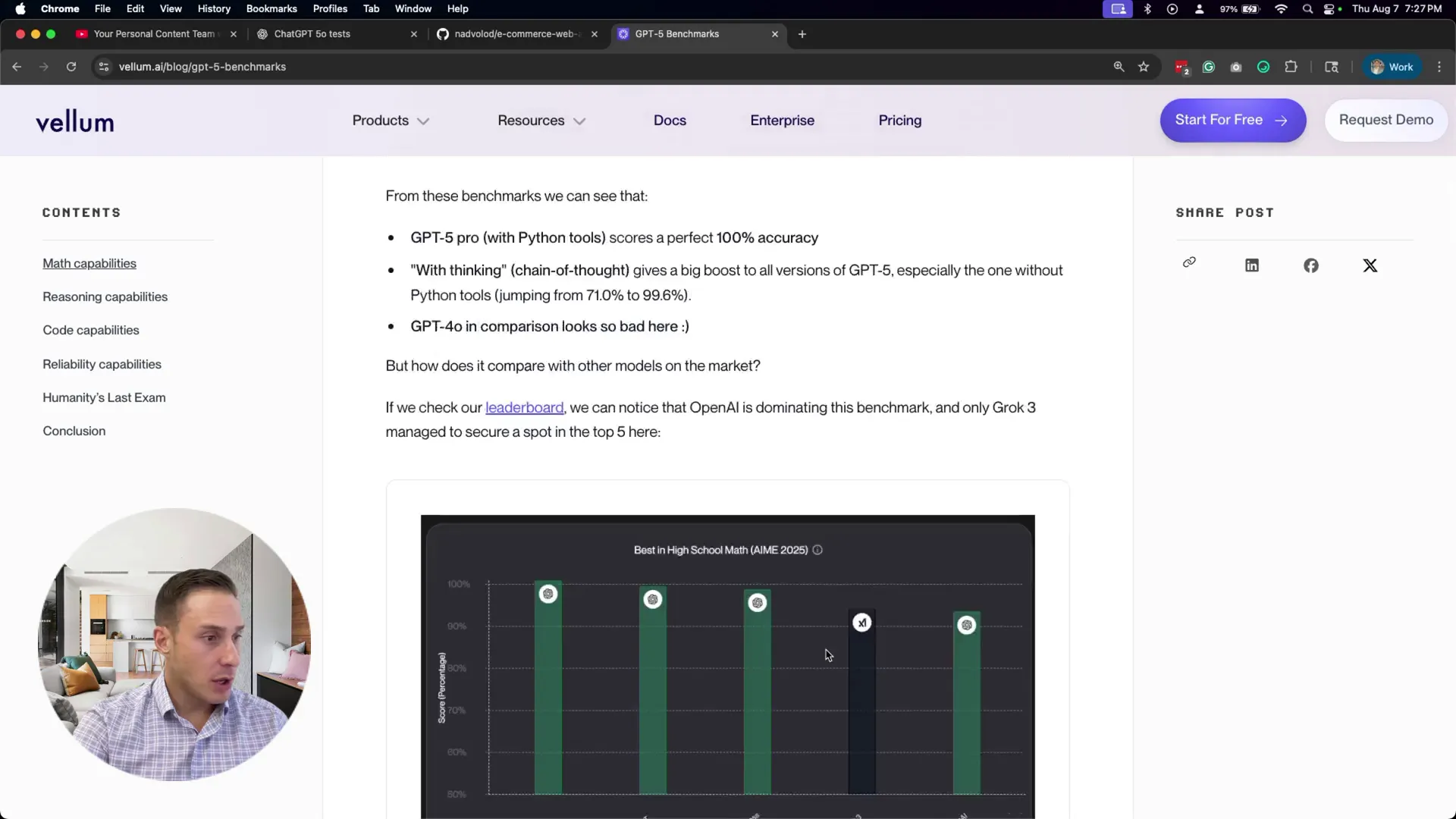
On the performance front, GPT-5 scores a flawless 100% on math capabilities—a critical factor for coding and algorithmic tasks. While the comparisons in the benchmark focus on OpenAI’s own models, GPT-5 also competes closely with other top-tier AI coding assistants like Claude and Grok, both renowned for their software engineering prowess.
One standout feature is GPT-5’s improved reliability, boasting significantly lower hallucination rates and fewer response errors, which means it provides more accurate and trustworthy outputs than its predecessors. This improvement is vital for developers who depend on AI for code generation and testing, as it reduces the need for constant manual corrections.
Putting GPT-5 to the Test: Debugging a Complex Web Application
To truly understand GPT-5’s capabilities, I decided to test it on a real-world challenge: pulling down and running a complex e-commerce web application built by GitHub Spark. This app forms part of a workshop I conduct on agentic tools and workflows for software development, testing, and deployment. While I had previously only run this application in GitHub’s cloud environment, I wanted to see if GPT-5 could help get it running locally, solve initial bugs, and improve its functionality.
Interestingly, I used the Cursor platform to interact with GPT-5 instead of ChatGPT’s pro version, which requires a costly subscription. Cursor provides access to GPT-5 without additional fees, making it a practical choice for developers like myself who are already investing heavily in AI tools.
Upon attempting to run the app locally, I immediately encountered errors related to missing GitHub Spark implementations—likely dependencies that only exist in the cloud environment. Here’s where GPT-5’s problem-solving skills shone. I tasked it with diagnosing and fixing these issues.
Much to my amazement, GPT-5 successfully identified the problematic package and replaced it with a suitable alternative, getting the app to start without crashing. Although the app didn’t fully load its UI components yet, this initial fix was a massive win given the complexity of dependency management and environment differences.
Automated UI Testing with Playwright: Successes and Struggles
With the app partially functional, I pushed GPT-5 further by asking it to implement a missing feature and then write automated UI tests to verify the fix using Playwright. Automated end-to-end testing is notoriously tricky for AI models, especially when it comes to writing meaningful assertions and avoiding redundant or ineffective test cases.
From previous experiences, many AI-generated tests tend to be either overly verbose, testing irrelevant interactions, or simply logging information without making real assertions. I was curious if GPT-5 could break this pattern.
Impressively, GPT-5 managed to write a suite of Playwright tests that performed sensible actions:
- Adding a to-do item and verifying its presence in the list
- Persisting to-dos across page reloads
- Checking toggle completion status and filter count updates
For example, it smartly assigned the to-do item “walk the dog” to a variable and then asserted its visibility on the page, which is a best practice in test writing. However, more complex tests—such as editing and deleting to-dos—were a bit more problematic. GPT-5 chose brittle XPath locators that are prone to breaking and struggled to correctly assert UI changes in these cases.
In the end, while GPT-5 was able to fix the core bug and generate useful automated tests, it got stuck on the more intricate browser testing tasks, spending too much time without a successful resolution. This suggests that although GPT-5 has made strides in automated testing, human oversight and refinement remain essential for complex UI scenarios.
Multimodal Testing: Generating Tests from Images
One of GPT-5’s novel features is its multimodal capability—meaning it can process and understand images alongside text. To explore this, I took a screenshot of the contact section from my personal website and uploaded it to Cursor, asking GPT-5 to generate automated UI tests based on that image.
The results were a mixed bag. GPT-5 correctly identified some UI elements such as headers, submit buttons, email input fields, and even reCAPTCHA frames. However, it also generated incorrect information, like a wrong contact URL, which would cause the tests to fail if run as is.
Moreover, the tests lacked depth and meaningful validation. They mostly checked for element existence rather than verifying functionality or user interactions. This experiment highlighted that while GPT-5’s multimodal testing shows promise, it’s still in its infancy and requires careful review before use in production environments.
Automated API Testing from Postman Collections
API testing is a critical component of modern software quality assurance. To test GPT-5’s ability here, I uploaded a Postman collection for a contact list API—created by Kristen Giacvoni, an expert in software testing—to see if GPT-5 could generate a reliable suite of automated API tests.
GPT-5 didn’t disappoint. It generated a comprehensive set of API tests covering the entire lifecycle of contacts:
- User registration and login
- Creating a contact
- Listing contacts and verifying the created contact is included
- Updating contact information
- Deleting a contact
These tests used appropriate HTTP methods and status code assertions, such as expecting 201 Created for successful resource creation. GPT-5 also smartly avoided hardcoding test data, which means these tests are more likely to work reliably on repeated runs.
Running these tests confirmed their solid implementation, showing GPT-5’s strength in generating meaningful and maintainable API test suites from existing documentation formats like Postman collections.
Designing a Beautiful Landing Page with Automated Tests
For the grand finale, I challenged GPT-5 to create a stunning, responsive landing page for our to-do app, complete with dynamic and interactive elements. The goal was to showcase the app’s features attractively and allow users to access the main application through this landing page.
GPT-5 designed a clean, modern UI with cool moving shapes and hover animations. The page was simple yet visually appealing, emphasizing usability and interactivity. However, it lacked images and some content felt empty, suggesting room for refinement.
Additionally, GPT-5 wrote automated UI tests for the landing page. While some tests, like verifying the visibility of headings and navigation to the app, were solid, others—such as checking animation on hover—were superficial. For instance, the test waited for an element to be visible but didn’t genuinely verify the animation effect, which could lead to false positives if left unchecked.
After implementing the landing page, the main to-do app broke due to some integration issues. GPT-5 helped identify and fix these errors, restoring functionality. This process demonstrated GPT-5’s ability to juggle multiple complex tasks, including UI design, test automation, and debugging.
Final Thoughts on GPT-5’s Capabilities and Future Potential
GPT-5 is undeniably a groundbreaking AI model that pushes the boundaries of what AI can do in software development and testing. From fixing complex bugs and generating automated Playwright tests to creating API test suites from Postman collections and designing interactive landing pages, GPT-5 showcased versatile and powerful capabilities.
However, the model is not without limitations. Automated UI testing remains challenging, especially for complex interactions and fragile locators. Multimodal testing from images still requires refinement to produce truly valuable and actionable tests. Human expertise is crucial to review, refine, and complement GPT-5’s outputs.
Nevertheless, GPT-5’s ability to follow instructions precisely and perform tasks as requested—without going beyond or falling short—is a significant step forward. Its lowered hallucination rates and improved reliability make it a trustworthy partner for developers aiming to automate and accelerate their workflows.
As AI models like GPT-5 continue to evolve, they will likely become indispensable tools in the software development lifecycle, transforming how we write code, test applications, and deliver high-quality software faster than ever before.
Frequently Asked Questions about GPT-5
What makes GPT-5 different from previous OpenAI models?
GPT-5 features a massive context window of 400,000 tokens and an output window of 128,000 tokens, allowing it to handle large, complex tasks in one go. It also boasts improved reasoning, coding abilities, and significantly lower hallucination rates, making it more reliable than earlier models.
Can GPT-5 write automated tests for both UI and APIs?
Yes, GPT-5 can generate automated UI tests using frameworks like Playwright and create comprehensive API test suites from Postman collections. While API test generation is robust, UI testing can still require human refinement, especially for complex interactions.
Does GPT-5 support multimodal inputs?
GPT-5 can process images alongside text, enabling it to generate tests based on screenshots. However, this feature is still developing and may not always produce fully accurate or valuable tests without manual review.
Is GPT-5 cost-effective for developers?
GPT-5 offers competitive pricing compared to other pro AI licenses, making it accessible for developers who need powerful AI capabilities without exorbitant costs. Platforms like Cursor provide access to GPT-5 without additional subscription fees.
How reliable is GPT-5 in fixing bugs and implementing new features?
GPT-5 excels at following instructions accurately and can fix complex bugs and implement new features effectively. However, it may struggle with intricate UI testing and some edge cases, so human oversight remains important.
Can GPT-5 design complete user interfaces?
Yes, GPT-5 can design responsive, modern landing pages with interactive elements. While the designs are clean and functional, they may require further enhancement and integration testing to ensure full application compatibility.
Weekly JavaScript Testing Tips:
https://ultimateqa.kit.com/js-testing-tips
